Have you ever felt that rush of euphoria after completing a workout, as if every cell in your body is celebrating? The journey of muscle growth is more than just lifting weights; it’s a transformative experience that intertwines mind and body. By engaging in resistance training, individuals push their physical limits, embracing the concept of progressive overload to challenge their muscles.
Each drop of sweat is a testament to their commitment. As they work towards greater strength, understanding muscle growth becomes crucial. It unveils a fascinating world of muscle hypertrophy, showcasing how the body repairs itself and flourishes through dedicated effort. Dive into this exploration of what truly happens during and after workouts. And if you need a bit more help in reaching your goals, Steroiden might be the answer!
What is Muscle Growth?

Muscle growth refers to the physiological process known as muscle hypertrophy, which entails the enlargement of muscle fibers as a result of physical training. This process enhances both functionality and aesthetics, offering individuals the ability to increase strength, speed, and endurance through effective exercise regimens. To understand muscle hypertrophy more comprehensively, one must consider its two primary types: myofibrillar hypertrophy and sarcoplasmic hypertrophy.
Definition of Muscle Hypertrophy
Muscle hypertrophy is defined as the increase in the size of skeletal muscle fibers, which occurs due to various forms of resistance training. As individuals engage in strength training, microscopic damage occurs within muscle fibers. This triggers repair mechanisms, resulting in thicker muscle fibers. Such transformations are paramount for athletes and fitness enthusiasts aiming to improve their physical capabilities and overall health.
Types of Muscle Hypertrophy

Understanding the distinctions between the types of muscle hypertrophy is vital for tailoring strength training programs. Each type serves different training goals:
| Type of Hypertrophy | Description | Key Benefits |
| Myofibrillar Hypertrophy | Focuses on the growth of contractile proteins in muscle fibers. | Increases strength and power. |
| Sarcoplasmic Hypertrophy | Enhances the volume of the sarcoplasm, which contains stored glycogen. | Improves muscular endurance and stamina. |
Incorporating both myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic hypertrophy into resistance training routines can lead to more comprehensive muscle development. By understanding these mechanisms, individuals can create tailored programs that align with their fitness aspirations.
Understanding Muscle Growth: The Mechanisms Behind It
The process of muscle growth encompasses several intricate physiological mechanisms. Each of these mechanisms plays a vital role in transforming the body and maximizing performance. Understanding the interplay between muscle loading, chemical reactions, and muscle repair through microtears can empower individuals to optimize their training routines.
Muscle Loading and Activation
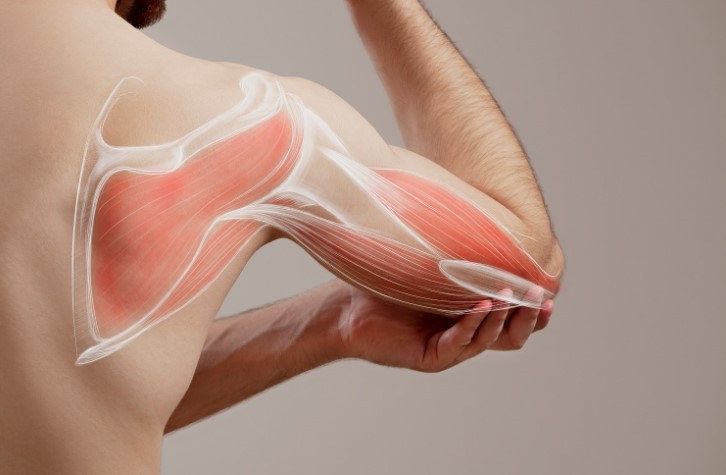
Muscle loading and activation begin when individuals engage in resistance training. This engagement triggers the central nervous system to initiate muscle contraction, leading to the activation of motor units. During intense workouts, the muscles undergo substantial stress, which necessitates adaptation and growth. Proper muscle activation is essential as it directly impacts the effectiveness of the workout.
Chemical Reactions During Workouts
During exercise, a series of complex chemical reactions unfold within the body. For example, the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) provides the necessary energy for muscle contractions. As muscles work, by-products such as lactic acid accumulate, signaling the need for recovery. These chemical reactions highlight the importance of efficient workout techniques to foster optimal muscle performance and growth.
The Role of Microtears in Muscle Repair
Microtears occur in muscle fibers as a result of strenuous exercise. This damage is a natural part of the muscle growth process. As the body begins to repair these microtears, satellite cells respond by multiplying and aiding in regeneration. The anabolic signaling pathway, particularly mTOR signaling, plays a crucial role in this recovery process, directing the synthesis of new proteins that promote increased muscle mass over time.
| Mechanism | Function | Significance |
| Muscle Loading | Initiates muscle contractions through resistance training | Promotes muscle adaptation and growth |
| Chemical Reactions | Provides energy through ATP breakdown | Facilitates muscle contraction and recovery |
| Microtears | Creates a need for muscle repair and growth | Essential for hypertrophy and increased muscle strength |
| mTOR Signaling | Regulates protein synthesis during recovery | Drives muscle growth and adaptation |
The Role of Nutrition and Recovery Strategies in Muscle Growth
Nutrition and recovery are foundational elements that significantly contribute to muscle growth. The process of protein synthesis is essential, as it relies on adequate levels of amino acids derived from a protein-rich diet to repair and rebuild muscle fibers following rigorous workouts. Understanding what to eat and when can maximize the body’s ability to recover and grow stronger.
Importance of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis acts as a critical biological process necessary for muscle repair. After engaging in strenuous physical activities, the body enters a recovery phase in which it uses amino acids to rebuild damaged muscle tissues. This rebuilding not only repairs but also enhances muscle size and strength, propelling fitness goals. Consuming sufficient protein is crucial for maximizing protein synthesis, especially in the hours following a workout.
Workout Nutrition: What to Eat and When

Effective workout nutrition centers on consuming the right nutrients at specific times to optimize recovery and performance. Aiming for about 20 grams of protein shortly after workouts provides the body with the amino acids it needs to kickstart the recovery process. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods, such as lean meats, dairy, legumes, and protein shakes, promotes a balanced and effective protein-rich diet. Timing the consumption of these foods can make a significant difference in enhancing muscular recovery.
Key Recovery Strategies for Optimal Muscle Repair
Implementing effective recovery strategies is vital to support muscle repair and growth. Factors such as hydration, adequate sleep, and structured rest days significantly enhance recovery processes. Active recovery practices, like low-intensity workouts or stretching, improve blood circulation and nutrient delivery to muscles. Below are some essential recovery strategies:
- Stay hydrated to facilitate nutrient transport and muscle function.
- Prioritize sleep to allow the body to undergo critical recovery processes.
- Incorporate active recovery techniques to keep blood flowing to muscles.
- Utilize foam rolling and stretching to alleviate tightness and foster flexibility.
| Recovery Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Hydration | Daily water intake to support metabolic functions. | Improves nutrient delivery to muscles, reduces soreness. |
| Sleep | Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. | Enhances recovery, hormone regulation, and muscle repair. |
| Active Recovery | Engage in low-intensity activity post-workout. | Promotes circulation, aiding in muscle recovery. |
| Stretching & Foam Rolling | Incorporate these practices post-exercise. | Reduces muscle tightness, improves flexibility. |
