
If you’re wondering how heat-resistant materials can help you survive a fire, read on. This article covers the basics of ceramics, metals, and Thermoset polymers. You’ll also learn about silicon nitride. Heat-resistant materials can withstand extreme temperatures and are resistant to fire. This means that even if a fire does start, it’ll take a very long time to burn.
1. Ceramics
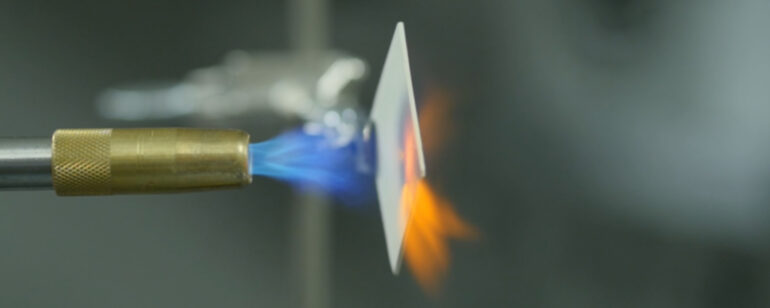
Many ceramics are used in a variety of applications, including dental restorations, dental implants, and hip replacements. Ceramics are used in these applications because of their high resistance to heat and corrosion and their ability to withstand body fluids. However, these materials have their downsides, so they should be used with care.
For example, metastable rocks can be brittle when exposed to extreme temperatures. However, by combining these materials, amorphous ceramics can overcome their brittleness. These fibers are processed similarly to carbon fibers, and Fraunhofer scientists are working with SGL Carbon in Wiesbaden to develop these materials on an industrial scale.
Another application for ceramics is in construction. While bricks and tiles remain popular in construction, ceramic tools are becoming increasingly common in this industry. Silicon carbide can be used for cutting glass, while silicon oxide is used for drilling through brick. These advanced ceramics can also be used to shape traditional ceramic materials.
Ceramics are also critical to the technological advancements of space travel. Future space vehicles will need materials that can withstand extreme temperatures. These materials are also used in many other components. And in the future, we will need ceramics for even more ambitious projects. The key is to develop materials that can withstand such extreme temperatures and still function.
Ceramics are used in a variety of products, from kitchen pantries to medical equipment. For example, ceramics are used in computer chips and capacitors. These materials also have the ability to bend.
2. Metals
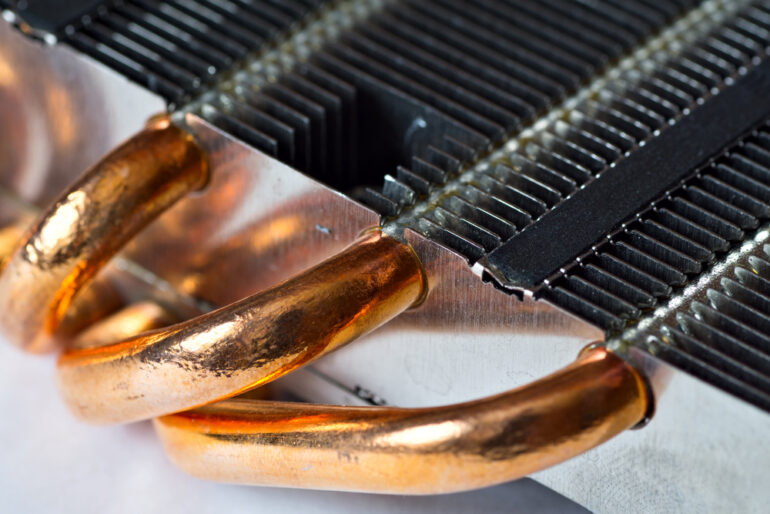

Heat-resistant metals can provide the ultimate protection in a range of applications. The materials are resistant to combustion products and gaseous chemicals and have excellent fatigue and creep strength at elevated temperatures. They also have a high modulus of elasticity, which increases their strength under dynamic loading. The low thermal expansion of these materials also helps improve their stress-rupture strength.
There are many different types of heat-resistant metals. Some are stronger than others and have a higher melting point. They also have excellent electrical conductivity, and they are highly corrosion-resistant. Some of the best-known heat-resistant metals are tungsten, tantalum, hafnium, iridium, platinum, and molybdenum.
Copper is another heat-resistant metal. Its antibacterial properties are highly beneficial, particularly for healthcare facilities, and learn more about it from ADL Insulflex. Copper can help to reduce microbial infections in areas where it is frequently used, such as sinks and faucets. Copper’s antimicrobial properties can also help prevent the spread of dangerous bacteria.
Moreover, it is a highly resilient material, which can withstand extreme temperatures and still retain its form. The properties of this metal make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. Some examples of applications include aircraft cabin heaters, automotive parts, and aerospace equipment. In fact, it has a high melting point, which makes it particularly useful for high-temperature applications.
Other metals that are heat-resistant include tungsten and titanium. Both are highly resistant to heat and can prevent corrosion when exposed to carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers. While some metals are more heat-resistant than others, they are not immune to oxidation and rust.
3. Thermoset polymers

Thermoset polymers are polymers with properties that help them survive the heat. These materials can withstand a wide range of temperatures. The reason for their superior heat resistance is the molecular structure of these polymers. Instead of aliphatic groups, thermoplastic polymers have rigid aromatic rings that restrict and strengthen their backbone. In addition to these polymers, wood is also a heat-resistant material.
Thermoset polymers are used for many applications. They are known for their high thermal stability and chemical resistance, which makes them suitable for many different industries.
Another advantage of thermoset polymers is their ability to be molded into any shape and remain stable at high temperatures. For these reasons, many manufacturers have shifted over to thermoset polymers for their manufacturing processes. They are also much cheaper and can be an excellent replacement for some metal components.
This material is resistant to chemicals and wear and is compatible with CNC machining. Thermoset polymers have high tensile strength and can withstand temperatures up to 120degC.
These materials are also excellent electrical insulators and are chemical-resistant. They are commonly used in automotive and aerospace parts. These thermoplastics can also be used in 3D printing. However, they must be designed to account for thermal expansion, which can limit geometric precision in 3D printing.
4. Silicon nitride

Silicon nitride has the potential to help heat-resistant materials survive even extreme temperatures. It is used in a variety of applications, from automotive components to high-pressure cryogenic pump bearings in NASA space shuttles. It has also been used to improve the performance of turbochargers and is often found in precision shafts.
One process for making HPSN is by hot isostatic pressing. This process begins with a silicon nitride powder and a densification aid. This mixture is then pressed with two punches under high pressure in a mold. The pressure from the punches aids the pore closure process. The high pressure of the process also helps the silicon nitride grains to grow in the direction that is normal to the pressing direction. This allows for higher density and greater stability.
Various types of silicon nitride can be created by using a reaction between silicon and nitrogen. Typically, commercial-grade silicon is used. The reaction produces a porous material that is strong. Its tensile strength at failure, known as the modulus of rupture (MoR), is very high. The four-point loading method is more thorough but produces less than the three-point method.
Oxidation resistance and thermal shock resistance are important properties in heat-resistant materials. This property is dependent on the material’s thermal conductivity, fracture strength, and Young’s modulus. Silicon nitride exhibits better thermal shock resistance than silicon carbide and other advanced ceramics.
One of the most interesting aspects of silicon nitride is its ability to resist high temperatures for a long period of time. Moreover, it is lightweight and can withstand high thermal loads. This feature has been verified by experiments.
5. ULTEM

If you want to survive the heat in your workplace, you should make use of ULTEM heat-resistant materials. These materials are known for their durability, flexibility, and fire resistance. They are also a cost-effective alternative for high-temperature applications. They are used in many applications such as hard disk drive internals, PCBs, Plenum Devices, and many other products.
ULTEM is a high-performance polymer designed to remain stable even when subjected to extreme temperatures. It is flame resistant and can withstand temperatures up to 217 degC. It is non-toxic and produces only a small amount of smoke. In addition to that, ULTEM is resistant to ultraviolet rays and gamma radiation.
ULTEM is widely used in electrical and automotive industries due to its excellent strength and temperature resistance. It is suitable for applications in high-temperature environments, and its dielectric strength is one of the highest among thermoplastics. It is also flame-resistant with the low smoke generation, making it a good choice for aircraft galley equipment.
Ultem is made of polyetherimide, which is a highly resistant polymer that resists oxidation and burning. Its dielectric strength makes it an excellent choice for applications in oil and gas as it can resist a wide range of chemicals. It is also suited to water and hot air environments.
The material is also known for its high strength and rigidity. It can withstand impact forces, punctures, and daily wear and tear. It is also remarkably flexible and can be used in many different membranes and containers. Its low weight and high heat resistance allow it to be used in several different industries.
